Pesticides >> Insecticide >>Teflubenzuron
Teflubenzuron 15%SC
Insecticide
benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name teflubenzuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO); no
name (the Netherlands)
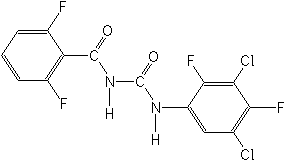
IUPAC name 1-(3,5-dichloro-2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[(3,5-dichloro-2,4-difluorophenyl)amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
CAS RN [83121-18-0] Development codes CME 134 (Celamerck)
Teflubenzuron APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor, affecting moulting. Mode
of action Non-systemic insect growth regulator with stomach action.
May affect fertility of female insects after contact or ingestion.
Uses Control of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Aleyrodidae, Hymenoptera,
Psyllidae, and Hemiptera larvae on vines, pome fruit, stone fruit,
citrus fruit, cabbages, potatoes, vegetables, soya beans, trees,
sorghum, tobacco, and cotton. Also controls fly and mosquito larvae,
and immature stages of major locust species. Also under development
to protect salmonids against sea lice. Formulation types SC; UL.
Selected tradenames: 'Nemolt' (BASF); 'Nomolt' (BASF)
Teflubenzuron OTHER TRADENAMES
'Calicide' (veterinary use) (BASF); 'Dart' (BASF); 'Diaract' (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Details of methods are available from BASF.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 71, 73 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute
oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not irritant to skin or eyes of rabbits.
Non-sensitising to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5058
mg dust/m3. NOEL (90 d) for rats 8 mg/kg b.w. daily, for dogs 4.1
mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1994]. Other Non-teratogenic.
Non-mutagenic in Ames, mammalian cell, and micronucleus assays.
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for
quail and ducks >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout and carp
>500 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees when used at recommended rates;
LD50 (topical) >1000 mg/bee. Other beneficial spp. Low toxicity
to predatory arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, teflubenzuron and
its metabolites are rapidly excreted in the faeces and urine. Three
metabolites have been identified in the urine (D. Eichler et al.,
6th Int. Congr. Pestic. Chem. IUPAC, 1986, Abstr. 7A-10). Plants
Almost no uptake and no metabolism in plants. Soil/Environment DT50
in soil 2-12 w. Microbial degradation occurs in soil, with rapid
metabolism to 3,5-dichloro-2,4-difluorophenylurea as the major metabolite.